Abstract
Place recognition is a core component of Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) algorithms. Particularly in visual SLAM systems, previously-visited places are recognized by measuring the appearance similarity between images representing these locations. However, such approaches are sensitive to visual appearance change and also can be computationally expensive. In this paper, we propose an alternative approach adapting LiDAR descriptors for 3D points obtained from stereo-visual odometry for place recognition. 3D points are potentially more reliable than 2D visual cues (e.g., 2D features) against environmental changes (e.g., variable illumination) and this may benefit visual SLAM systems in long-term deployment scenarios. Stereo-visual odometry generates 3D points with an absolute scale, which enables us to use LiDAR descriptors for place recognition with high computational efficiency. Through extensive evaluations on standard benchmark datasets, we demonstrate the accuracy, efficiency, and robustness of using 3D points for place recognition over 2D methods.
Method
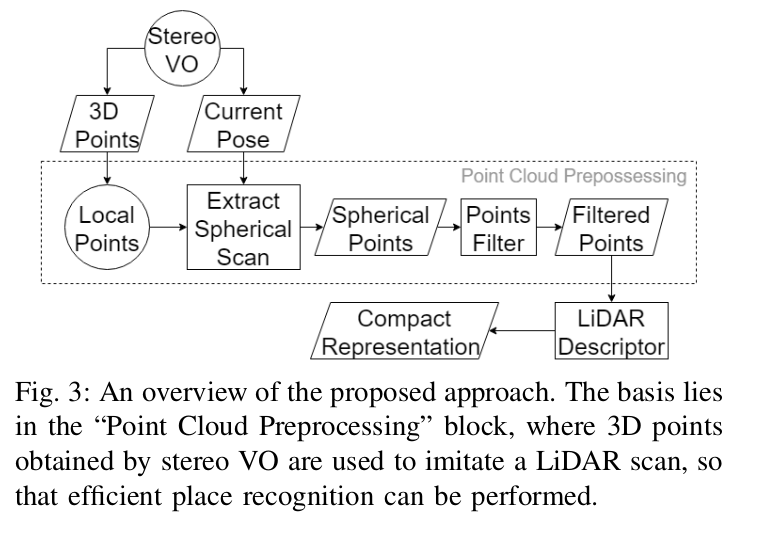
LiDAR Descriptors
1. DELIGHT
2. M2DP augmented with grayscale intensity
3. Scan Context augmented with grayscale intensity
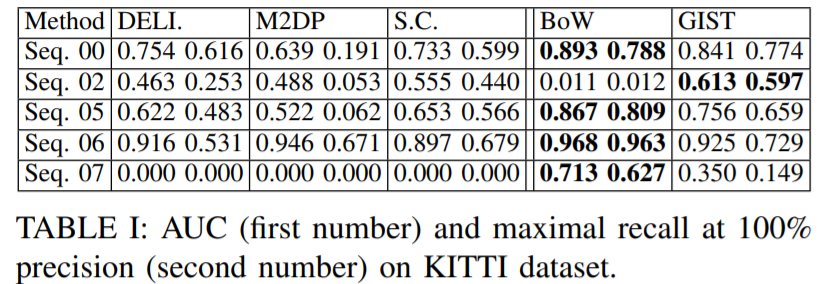
Results on KITTI dataset
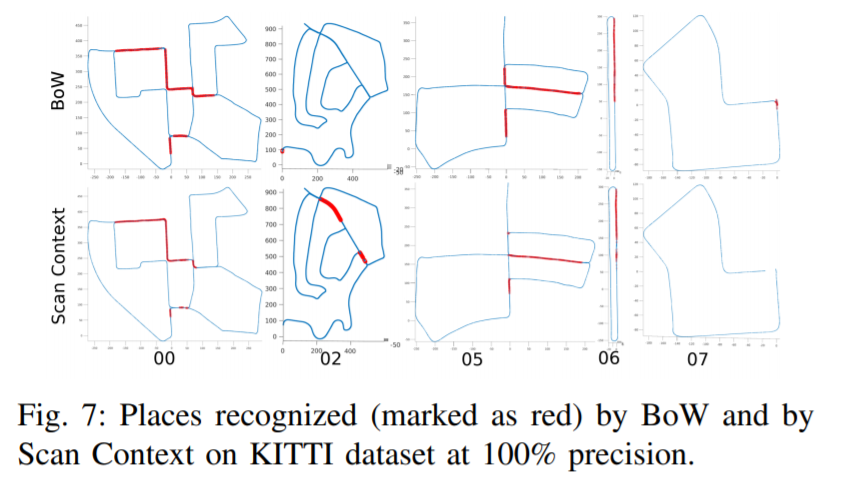

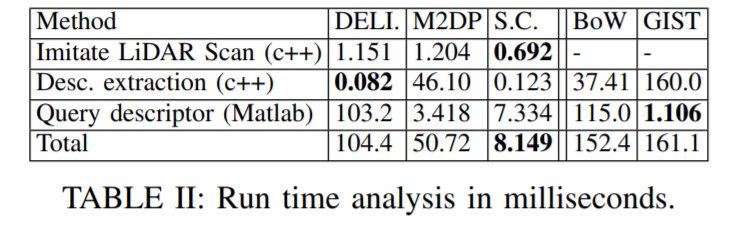
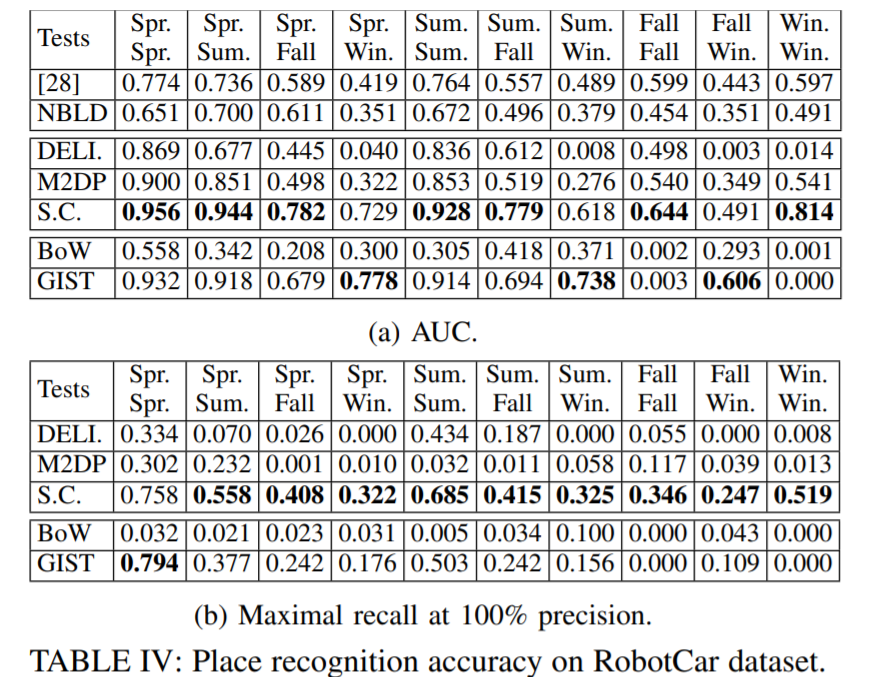
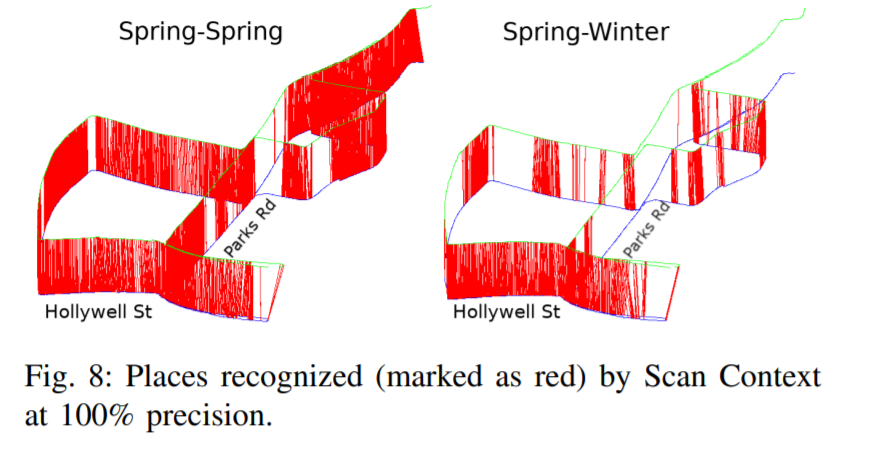
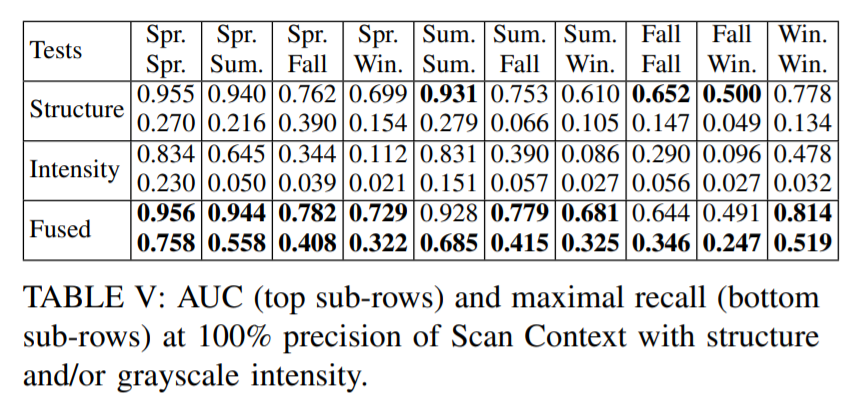
Results on Oxford RobotCar dataset

Links
Paper(IROS20)